AI comes to the farm: New technology tackles acres of weeds quickly by using robotics and lasers
LaserWeeder by Seattle-based Carbon Robotics rids farms of weeds, said CEO Paul Mikesell
Farmers interested in a fast, accurate way to rid their fields of weeds have a new option in the AI space. Carbon Robotics is now shipping its LaserWeeder to farms around the United States; the machine uses the power of lasers and robotics to rid fields of weeds.
Weeds are one of the most "tedious, time-consuming and challenging" elements of farming, Carbon Robotics told Fox Business via email.
The LaserWeeder can eliminate over 200,000 weeds per hour and offer up to 80% cost savings in weed control.
Carbon Robotics CEO and founder Paul Mikesell "knows farmers and has a lot of friends who are farmers," he said.
ALPHABET EXEC: 'AI AUTOMATES TASKS, NOT JOBS'
He decided to use his background in computer science, AI deep learning and business to create the LaserWeeder, he told Fox Business in a recent interview.
"We grow a fair amount of vegetables up here between Washington, California, Oregon and Idaho," said Mikesell, whose company is in Seattle.
The "match that lit the fire" in developing the LaserWeeder was realizing that "this venture capital money that is going into AI and technology — none of it was flowing into agriculture, and I didn't understand why," he said.
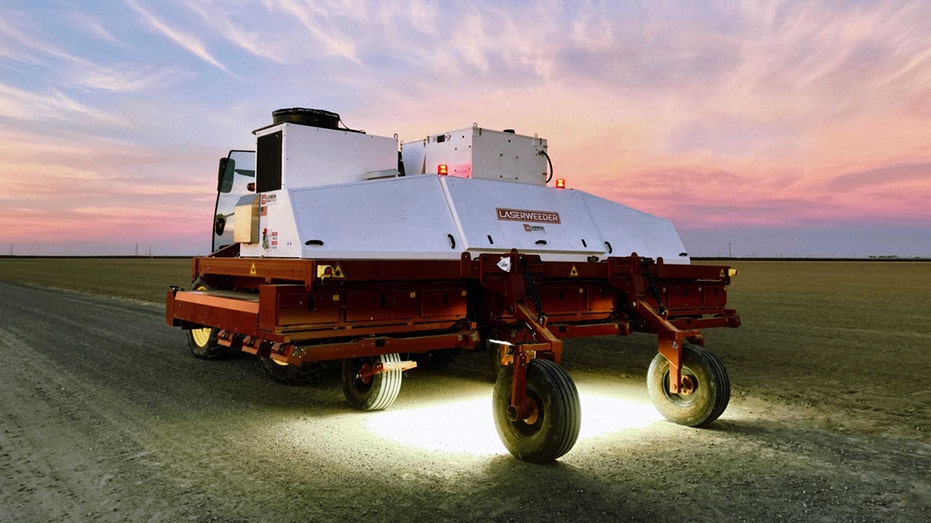

The LaserWeeder, by Carbon Robotics can get rid of 200,000 weeds per hour, the company told Fox Business. Above, an early commercial demo model is shown. The unit for sale is pulled behind a tractor. (Carbon Robotics / Fox News)
Calling it a "huge gap," Mikesell decided to develop an AI-powered agricultural tool to identify and remove weeds on a large scale.
The LaserWeeder is a 20-foot-wide unit comprised of three rows of 10 lasers that are pulled behind a tractor.
Thirty lasers are at work as the unit travels across a field destroying weeds "with millimeter accuracy, skipping the plant and killing the weed," said Mikesell.
CRYPTO SCAMS AGAINST SENIORS SURGED 78% IN 2022
The LaserWeeder "does the equivalent work of about 70 people," he continued.
He noted that the tool employs a "process of thermal energy. Thermal energy cell disruption is what's happening at the plant level." (SEE the LaserWeeder at work in the video below.)
This is "good for labor costs" and also "good for farmers struggling with labor availability," Mikesell said.
"We taught it the difference between the different species of weeds," he said of the unit. "We taught it how to protect the crops and not treat the crops."
He continued, "We taught it how to understand the size of a weed, not just in terms of the area, but also how thick it is. Then we plug that neural net — that deep learning AI — into a bunch of lasers and we let it kill weeds."
SUMMER OF THROWBACKS: COMPANIES LOOK TO CAPITALIZE ON CLASSIC '90S PRODUCTS, MOVIES
The LaserWeeder "sees everything that's on the field," he said.
It works without harmful herbicides or chemicals, he also said.
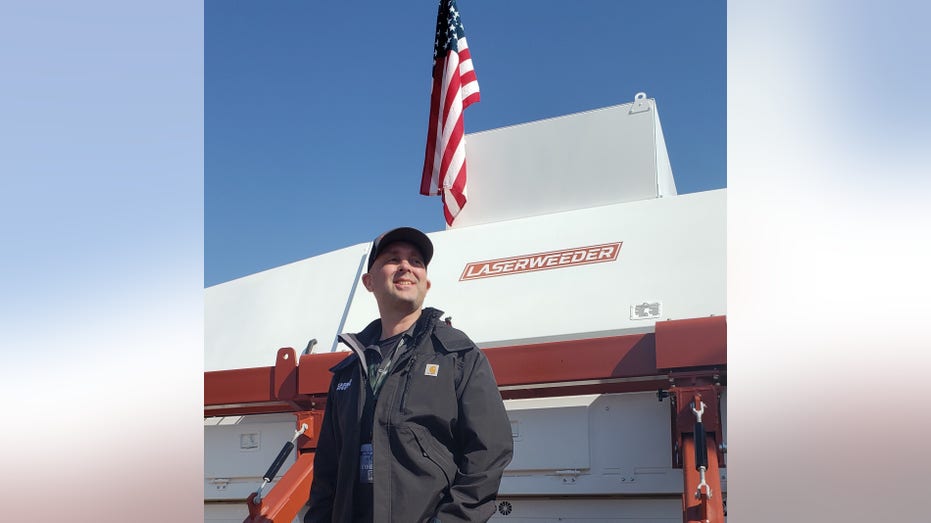

Carbon Robotics CEO and founder Paul Mikesell stands in front of a LaserWeeder unit. As homeowners know, weeds are "always coming in, more and more of them, as part of the natural process," said Mikesell. (Carbon Robotics / Fox News)
"You don't have to have people out there pulling the weeds," he also said.
The technology "makes for a much more consistent growing process and adds a bunch of health to your yield. You get big yield improvements because you're not damaging the crops with herbicides."
A farmer will use the LaserWeeder yearly, he said.
"People just didn't realize how much opportunity there was in farming."
"We can't kill all the weeds because those weed seeds will live in the soil for seven years," he explained.
As homeowners know, weeds are "always coming in, more and more of them, as part of the natural process," said Mikesell.
FOURTH OF JULY TRAVEL IS EXPECTED TO BREAK RECORDS
"They're blowing through the air. They're coming in through the water system. They're running down the streams and rivers. They're part of the irrigation cycle, in a lot of cases."
He added, "And so it's a continual process — in the same way that people have field workers in the fields every year, or they spray herbicides every year, you would do the same thing with the LaserWeeder."
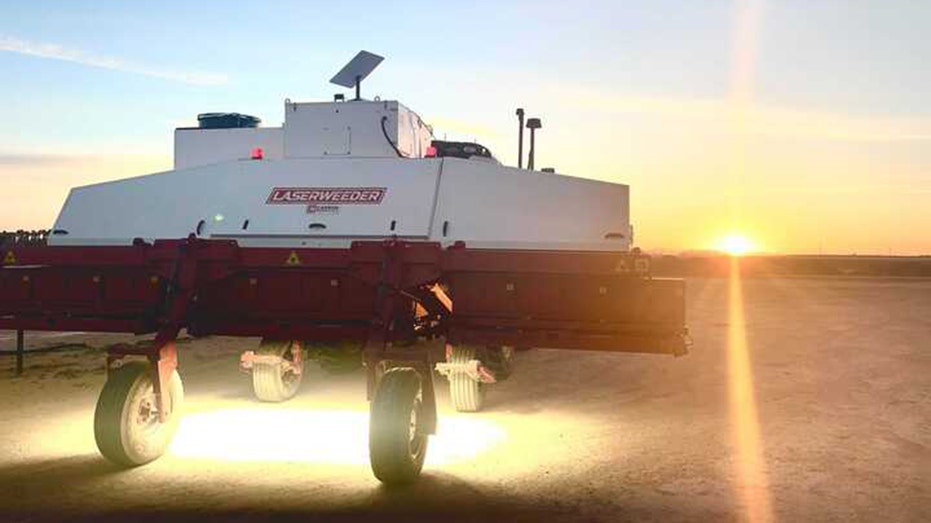

Carbon Robotics, based in Seattle, Washington, uses the power of AI, robotics and lasers to help farmers combat weeds. (Carbon Robotics / Fox News)
The adoption by the farming community "has been great," said its CEO, noting that the company is "spending a lot of time with farmers, to make sure we're building what they need."
What does Mikesell think about AI in general?
"I would say the concerns I have would be things like privacy and surveillance," he replied.
TEXAS WOMAN SAYS SHE BOUGHT $1.25 JACKET AT GOODWILL WORTH HUNDREDS, REVEALS HER BEST THRIFT HAULS
He added, "In the same way that we can tell weeds from plants very accurately, very quickly — others can use AI to identify very quickly who you are."
The positives of AI, according to Mikesell, are that it will be producing "really great tools for the rest of us."

In this June 16, 2021, file photo, an irrigation canal runs past farmland in Lemoore, California. Irrigation is one way weeds are spread, said Carbon Robotics CEO and founder Paul Mikesell. (AP Photo/Noah Berger, File / AP Newsroom)
Farming "is one of the most important things that we do" as a society, said Mikesell.
"Farming is where your food comes from."
CLICK HERE TO GET FOX BUSINESS ON THE GO
The CEO said he believes that the reason AI is taking so long to get into the farming space is that much of AI technology "was developed in these urban centers and focused on the kinds of problems that folks have in the cities."
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR LIFESTYLE NEWSLETTER
He added, "People just didn't realize how much opportunity there was in farming — that gap has happened for a number of reasons and has gone on for too long. So we're here to help bridge that."