Mediterranean diets may reduce the risk of dementia up to 35%: study
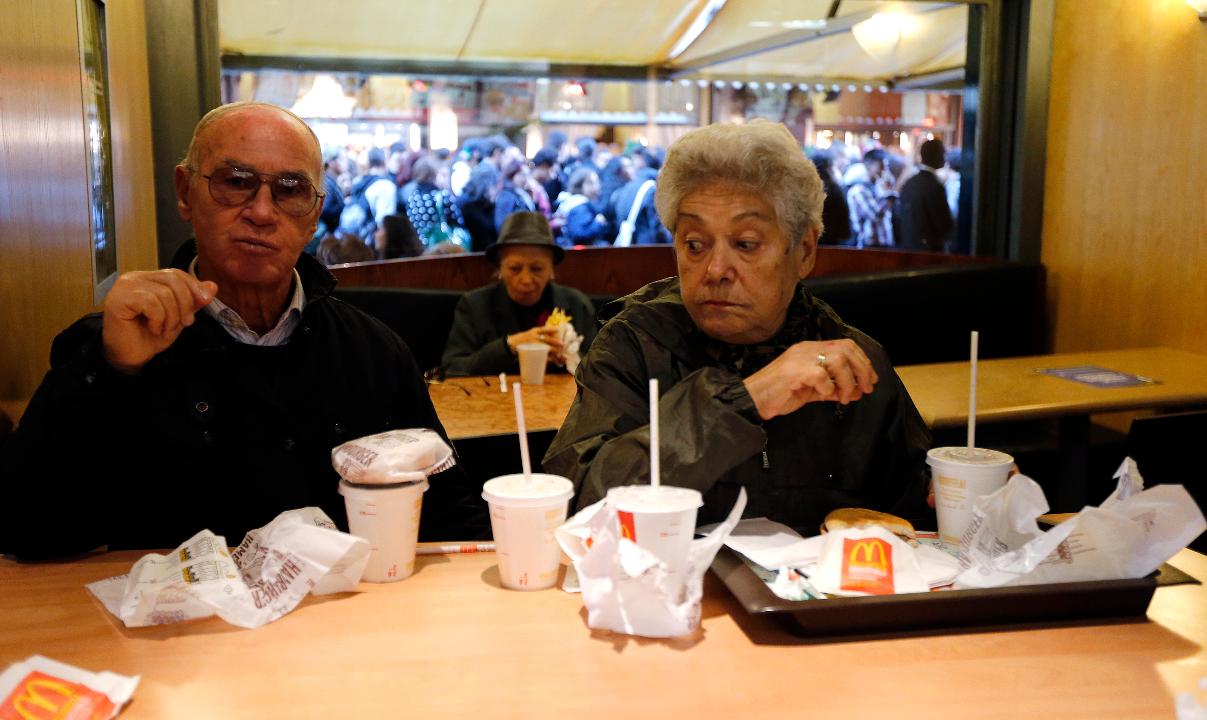
Healthy eating habits, particularly the Mediterranean diet, which was originally developed to improve cardiovascular health, may lower your risk of developing cognitive impairment up to 35%, the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference said Monday.
A group of U.S. scientists, who studied the diets of 6,000 older adults, found that those who consistently followed a Mediterranean diet or a MIND diet—full of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains -- had a 30% to 35% lower risk of developing cognitive impairment later on in life.
“[Today] we confirm everything that we’ve known, that changing your dietary pattern is actually quite impactful and you can change your trajectory of cognitive decline—if you adhere to a Mediterranean diet or other diets that are low in saturated fats, processed flour and sugar,” Maria Carrillo, Ph.D., chief science officer at the Alzheimer’s Association (ALZ) tells FOX Business.
Researchers from the Karolinska Institute in Sweden also found that people who stuck to a healthy Nordic diet that consists of non-root vegetables, certain fruits, fish and poultry enjoyed a better cognitive status than individuals who ate a less healthy diet. Another study from Wake Forest School of Medicine in North Carolina found that women in particular are less likely to develop Alzheimer’s, an irreversible progressive brain disorder, if they stuck with a healthy diet.
Today, over 5.5 million Americans are living with Alzheimer’s and that number is expected to rise to 15 million by 2050, according to the Alzheimer’s Association.
Carrillo says that rise could be attributed to the rise of fast food in the U.S. and other countries around the world in recent decades.
“People that perhaps eat a lot of junk food and processed foods may end up having less brain cognition over time as they age and may actually have smaller brains,” Carrillo says.
Additionally, Carrillo says other lifestyle factors such as exercise, sleep, and reducing stress also play a role in cognitive health.